Oral–Systemic Health
SFG convenes and collaborates with partners to translate evidence into action—advancing medical-dental integration, preventive oral health, and equity-focused policy. Use this page to explore condition-specific evidence and share actionable tools that connect oral health to overall wellness.
Why Oral–Systemic Health Matters
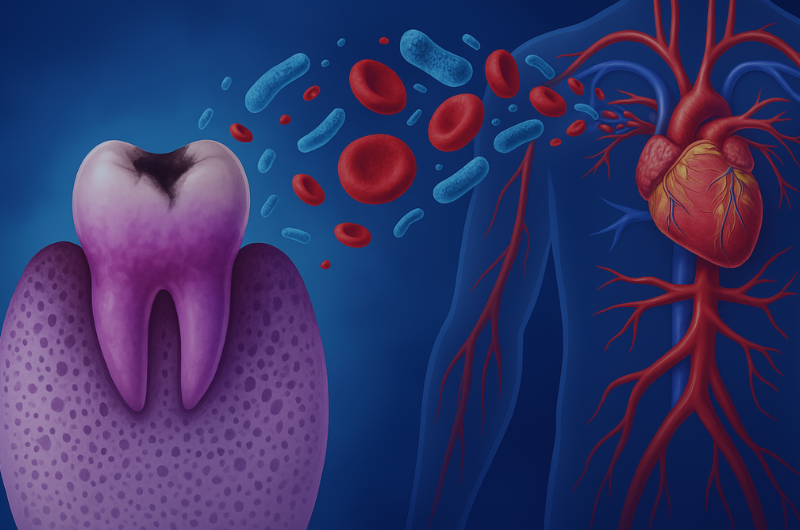
Oral inflammation and infection are linked with cardiometabolic risk, pregnancy outcomes, respiratory complications, and cancer treatment effects. Recognizing the bidirectional relationships between oral health and systemic disease helps interprofessional teams prevent avoidable harm, reduce costs, and improve quality of life—especially for populations facing barriers to care.
This hub curates high-value summaries and toolkits you can use across newsletters, education, and advocacy—making it easier to align clinical practice, public messaging, and policy.
Understanding the Oral–Systemic Connection
The oral–systemic connection describes the relationship between oral conditions—especially inflammation and infection—and chronic diseases throughout the body. Evidence now links poor oral health to diabetes, cardiovascular disease, respiratory illness, adverse pregnancy outcomes, and even certain cancers. Bacteria and inflammatory mediators that originate in the mouth can influence systemic pathways, affecting immunity, metabolism, and vascular health.
Recognizing these links shifts oral health from a siloed specialty to an essential component of whole-person care. Coordinated prevention and early intervention—regular dental visits, tobacco cessation, nutrition counseling, and periodontal therapy—can improve chronic-disease outcomes and lower healthcare costs. This alignment of medical and dental teams is known as medical–dental integration (MDI), a cornerstone of modern preventive care.
From an equity standpoint, the oral–systemic framework reveals how social and structural factors affect both oral and overall health. Populations that face barriers to dental coverage, transportation, or health literacy also experience higher rates of systemic disease. Addressing these shared social determinants advances oral health equity while improving population health.
Through its role as a convener and facilitator, the Santa Fe Group brings together researchers, academics, clinicians, policymakers, and public-health advocates to accelerate integration. By sharing research evidence, actionable toolkits, and policy guidance, SFG drives change through collective action—turning knowledge about the oral–systemic link into measurable improvements in prevention, access, and wellness.
The Santa Fe Group’s Role
We convene cross-sector leaders to turn evidence into action—advancing medical–dental integration, prevention, and equity. Explore our work:
Featured Evidence & Resources
Latest News & Insights
Explore Key Resources
Diabetes & Metabolic Health
Periodontal inflammation can worsen glycemic control, while improved oral health supports better outcomes. Integrate screening questions, referral pathways, and preventive hygiene for people with prediabetes and diabetes.
Heart Disease & Stroke
Shared risk factors—tobacco use, diet, and inflammation—connect oral health with cardiovascular outcomes. Coordinated prevention and risk counseling across dental and medical settings can reduce events and costs.
Cancer & Treatment Effects
Chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies can affect oral tissues, salivary glands, and microbiome balance. Proactive oral care reduces complications and supports treatment adherence.
Pregnancy & Maternal Health
Dental care is safe during pregnancy. A healthy mouth supports nutrition, comfort and infection control. Integrated care pathways and counseling can reduce missed opportunities for prevention. These resources explore how collaborative models improve access for expecting parents and strengthen dental–medical integration in maternal care.
Integration & Prevention
Medical-Dental integration translates evidence into workflows: shared screening, referral directories, care coordination, and patient education. Start with small, repeatable steps that fit your team’s capacity and expand from there.
Toolkits & Resources
Ready-to-use materials from SFG to implement the oral–systemic connection in practice, policy, and communications.
Campaign Kits
- Oral Cancer Awareness — Early Detection explainer · Awareness Month article
- Diabetes & Gum Health — Evidence summary (PDF)
- Pregnancy & Oral Health — Call to Action resource
Clinician Tools
Join the Movement
Help us advance oral–systemic health through research translation, policy, and partnerships.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the oral–systemic connection?
The evidence-based relationship between oral conditions—particularly inflammation and infection—and systemic health, including diabetes, cardiovascular disease, respiratory illness, adverse pregnancy outcomes, and cancer treatment effects.
How should teams use this page?
As a curated starting point: adapt talking points for patient education, embed toolkits in quality improvement, and share links across professional education, clinical workflows, and policy advocacy.
How does this support SFG’s role?
SFG acts as a convener and facilitator, aligning researchers, academics, clinicians, and policymakers to translate evidence into integration, prevention, and equity-focused action.
What evidence links periodontal disease with diabetes outcomes?
Periodontal inflammation is associated with higher A1c and poorer glycemic control; coordinated hygiene, risk counseling, and timely periodontal therapy support effective diabetes management.
Which oral conditions are most associated with cardiovascular risk?
Periodontitis and oral infections are most studied; reducing inflammatory burden alongside tobacco cessation and nutrition counseling aligns with cardiometabolic risk reduction.
What clinical workflows support dental–medical integration in primary care?
Use standardized oral-health screening, embedded referral directories, warm handoffs, and closed-loop tracking; start small, make processes repeatable, and surface them in the EHR.
What quality measures can teams use to track progress?
Decrease in evidence of periodontal disease, improvement in hemoglobin A1C, fewer hospitalizations and lower costs, and smoking cessation.
How should oncology teams coordinate oral care before and during treatment?
Schedule pre-treatment dental assessment, optimize oral hygiene, and rapidly manage infection to reduce complications and support adherence to cancer therapy.
What data elements enable effective closed-loop referrals?
Capture oral-health risk, reason for referral, appointment status, and outcomes; align privacy and security practices so dental and medical teams can exchange essentials.
Page last updated: February 2, 2026